PydanticAI 架构设计
本章概览
本章将深入解析 PydanticAI 的整体架构设计,帮助你理解:
- 核心组件及其职责
- Agent 执行流程
- 类型系统设计
- 与 LangGraph 架构的对比
1. 整体架构
1.1 分层架构
PydanticAI 采用清晰的分层设计:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Application Layer │
│ (应用层) │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ User Code │ │
│ │ 开发者编写的业务逻辑 │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Agent Layer │
│ (Agent 层) │
│ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌──────────────┐ │
│ │ Agent │ │ Tools │ │ Output │ │ Dependencies │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ Types │ │ │ │
│ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────┘ └──────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Model Layer │
│ (模型抽象层) │
│ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Model Interface │ │
│ │ 统一的模型交互接口 │ │
│ └──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Provider Layer │
│ (提供商适配层) │
│ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ ┌─────────┐ │
│ │ OpenAI │ │Anthropic│ │ Gemini │ │ Ollama │ ... │
│ └─────────┘ └─────────┘ └─────────┘ └─────────┘ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘1.2 核心组件
| 组件 | 职责 | 类比 |
|---|---|---|
| Agent | 核心控制器,编排所有交互 | FastAPI 的 Router |
| Tools | LLM 可调用的函数 | FastAPI 的 Endpoints |
| Dependencies | 运行时注入的依赖 | FastAPI 的 Depends |
| Output Types | 结构化输出定义 | FastAPI 的 Response Models |
| Model | LLM 抽象接口 | 数据库 ORM |
| Provider | 具体 LLM 实现 | 数据库驱动 |
2. Agent 核心架构
2.1 Agent 类设计
Agent 是 PydanticAI 的核心类,它是一个泛型类:
python
class Agent(Generic[DepsT, OutputT]):
"""
Agent[DepsT, OutputT]
- DepsT: 依赖类型,通过 deps_type 参数指定
- OutputT: 输出类型,通过 output_type 参数指定
"""
def __init__(
self,
model: str | Model, # 模型标识或实例
*,
output_type: type[OutputT] = str, # 输出类型
deps_type: type[DepsT] = None, # 依赖类型
instructions: str = None, # 系统指令
tools: list[Tool] = None, # 工具列表
model_settings: ModelSettings = None, # 模型配置
):
...2.2 Agent 内部结构
┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Agent │
├──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Configuration │ │
│ │ • model: 使用的 LLM │ │
│ │ • instructions: 系统指令 │ │
│ │ • model_settings: 模型参数 (temperature, max_tokens) │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Type Definitions │ │
│ │ • deps_type: 依赖类型定义 │ │
│ │ • output_type: 输出类型定义 │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Registered Tools │ │
│ │ • @agent.tool 装饰的函数 │ │
│ │ • @agent.tool_plain 装饰的函数 │ │
│ │ • 构造函数传入的 tools │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ │ Registered Prompts │ │
│ │ • @agent.system_prompt 装饰的函数 │ │
│ │ • @agent.instructions 装饰的函数 │ │
│ └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
└──────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘2.3 Agent 执行方法
Agent 提供多种执行方式:
python
# 1. 异步执行
result = await agent.run('prompt', deps=my_deps)
# 2. 同步执行(内部使用事件循环)
result = agent.run_sync('prompt', deps=my_deps)
# 3. 流式输出
async with agent.run_stream('prompt', deps=my_deps) as stream:
async for chunk in stream.stream_text():
print(chunk, end='')
# 4. 流式事件
async with agent.run_stream_events('prompt', deps=my_deps) as stream:
async for event in stream:
print(event)
# 5. 迭代控制(高级)
async with agent.iter('prompt', deps=my_deps) as run:
async for node in run:
# 手动控制每个节点
pass3. 执行流程
3.1 基本执行流程
 图:PydanticAI Agents 官方文档页面
图:PydanticAI Agents 官方文档页面
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ Agent.run() 执行流程 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
用户调用
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. 准备阶段 │
│ • 解析依赖 (deps) │
│ • 构建系统提示 (instructions) │
│ • 收集所有工具定义 │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 2. 请求阶段 │
│ • 构建消息列表 (messages) │
│ • 发送请求到 LLM │
│ • 处理流式/非流式响应 │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ LLM 响应 │
└──────┬──────┘
│
┌───────────┴───────────┐
▼ ▼
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 纯文本响应 │ │ 工具调用请求 │
└────────┬────────┘ └────────┬────────┘
│ │
│ ▼
│ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ 3. 工具执行 │
│ │ • 解析参数 │
│ │ • 验证参数 │
│ │ • 执行工具 │
│ │ • 收集结果 │
│ └────────┬────────┘
│ │
│ ▼
│ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ 发送工具结果 │
│ │ 到 LLM │
│ └────────┬────────┘
│ │
│ └─────────┐
│ │
│ 循环直到无工具调用
│ │
└───────────────┬──────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 4. 输出验证阶段 │
│ • 解析 LLM 最终响应 │
│ • Pydantic 验证输出类型 │
│ • 验证失败则触发重试 │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 5. 返回结果 │
│ • 包装为 RunResult / StreamedRunResult │
│ • 包含输出、消息历史、使用统计 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘3.2 内部节点模型
PydanticAI 使用 pydantic-graph 管理执行状态:
python
# 内部节点类型
class UserPromptNode:
"""用户输入节点"""
pass
class ModelRequestNode:
"""模型请求节点"""
pass
class CallToolsNode:
"""工具调用节点"""
pass
class End:
"""结束节点,包含最终结果"""
pass执行图示意:
UserPromptNode ──► ModelRequestNode ──► CallToolsNode ──► ModelRequestNode ──► End
│ ▲ │
│ │ │
└── 有工具调用 ────────┘ │
│
└──────────── 无工具调用 ─────────────────┘4. 类型系统
4.1 泛型设计
PydanticAI 大量使用 Python 泛型确保类型安全:
python
from typing import Generic, TypeVar
from pydantic import BaseModel
# 类型变量
DepsT = TypeVar('DepsT') # 依赖类型
OutputT = TypeVar('OutputT') # 输出类型
# Agent 是双参数泛型
class Agent(Generic[DepsT, OutputT]):
...
# RunContext 是单参数泛型
class RunContext(Generic[DepsT]):
deps: DepsT # 类型安全的依赖访问
...
# 使用示例
from dataclasses import dataclass
@dataclass
class MyDeps:
api_key: str
user_id: int
class MyOutput(BaseModel):
answer: str
confidence: float
# 完整类型注解
agent: Agent[MyDeps, MyOutput] = Agent(
'openai:gpt-4o',
deps_type=MyDeps,
output_type=MyOutput,
)4.2 输出类型支持
PydanticAI 支持多种输出类型:
python
# 1. 简单类型
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=str)
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=int)
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=bool)
# 2. Pydantic 模型
class UserInfo(BaseModel):
name: str
age: int
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=UserInfo)
# 3. 列表类型
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=list[str])
# 4. 联合类型
from typing import Union
class Success(BaseModel):
result: str
class Failure(BaseModel):
error: str
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=Union[Success, Failure])
# 5. TypedDict
from typing import TypedDict
class Config(TypedDict):
host: str
port: int
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', output_type=Config)4.3 输出模式
PydanticAI 提供三种输出实现方式:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 输出模式对比 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ Tool Output (默认) │
│ ───────────────── │
│ • 使用工具调用返回结构化数据 │
│ • 几乎所有模型都支持 │
│ • 最可靠的方式 │
│ │
│ Native Output │
│ ───────────── │
│ • 使用模型原生 "Structured Outputs" 功能 │
│ • 仅部分模型支持 (OpenAI, Gemini) │
│ • 性能最好 │
│ │
│ Prompted Output │
│ ─────────────── │
│ • 将 JSON Schema 注入提示词 │
│ • 所有模型都支持 │
│ • 可靠性较低 │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘5. 模型抽象
5.1 模型标识符
PydanticAI 使用简洁的字符串格式标识模型:
格式: provider:model_name
示例:
openai:gpt-4o
anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-0
google-gla:gemini-1.5-pro
ollama:llama3.2
bedrock:us.anthropic.claude-3-5-sonnet-20241022-v2:0 图:PydanticAI 支持的模型提供商
图:PydanticAI 支持的模型提供商
5.2 模型层次结构
┌─────────────────┐
│ Model │
│ (抽象基类) │
└────────┬────────┘
│
┌────────────────────┼────────────────────┐
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ OpenAIModel │ │AnthropicModel │ │ GeminiModel │
└───────────────┘ └───────────────┘ └───────────────┘
│ │ │
▼ ▼ ▼
┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
│ Provider │ │ Provider │ │ Provider │
│ (API 客户端) │ │ (API 客户端) │ │ (API 客户端) │
└───────────────┘ └───────────────┘ └───────────────┘5.3 回退模型
支持多模型回退机制:
python
from pydantic_ai import Agent
from pydantic_ai.models import FallbackModel
# 创建回退模型
fallback = FallbackModel(
'anthropic:claude-sonnet-4-0', # 主模型
'openai:gpt-4o', # 备用模型 1
'google-gla:gemini-1.5-pro', # 备用模型 2
)
agent = Agent(fallback)
# 如果主模型失败 (4xx/5xx),自动尝试下一个
result = agent.run_sync('Hello')6. 工具系统
6.1 工具注册方式
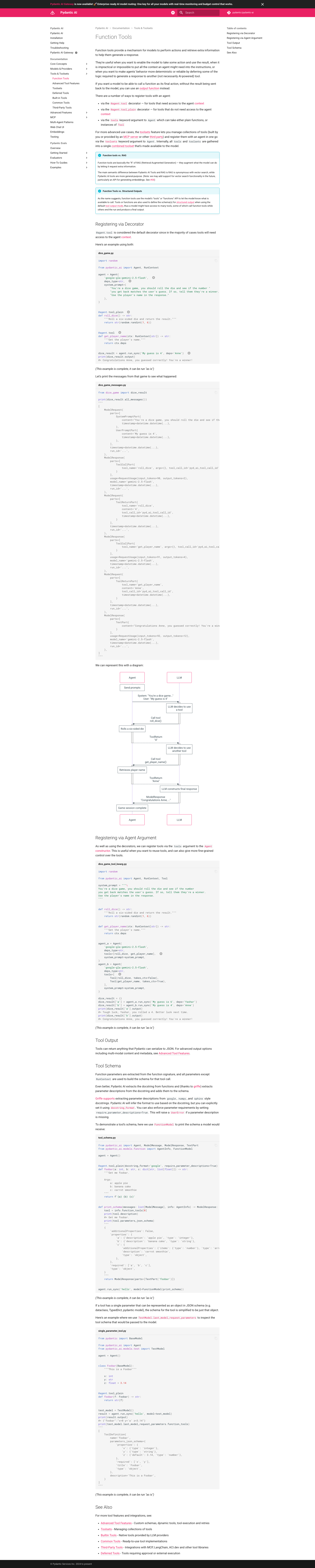 图:PydanticAI Tools 官方文档
图:PydanticAI Tools 官方文档
python
from pydantic_ai import Agent, RunContext
agent = Agent('openai:gpt-4o', deps_type=str)
# 方式 1: @agent.tool - 需要访问上下文
@agent.tool
async def get_user_name(ctx: RunContext[str]) -> str:
"""获取用户名称"""
return ctx.deps
# 方式 2: @agent.tool_plain - 不需要上下文
@agent.tool_plain
def calculate(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""计算两数之和"""
return a + b
# 方式 3: 构造函数传入
from pydantic_ai import Tool
def my_tool(x: str) -> str:
"""我的工具"""
return x.upper()
agent = Agent(
'openai:gpt-4o',
tools=[Tool(my_tool)]
)6.2 工具 Schema 生成
PydanticAI 自动从函数签名生成工具 Schema:
python
@agent.tool_plain
def search_database(
query: str, # 必需参数
limit: int = 10, # 可选参数,默认 10
include_deleted: bool = False, # 可选参数,默认 False
) -> list[dict]:
"""
搜索数据库记录
Args:
query: 搜索关键词
limit: 返回结果数量限制
include_deleted: 是否包含已删除记录
"""
...自动生成的 Schema:
json
{
"name": "search_database",
"description": "搜索数据库记录",
"parameters": {
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"query": {
"type": "string",
"description": "搜索关键词"
},
"limit": {
"type": "integer",
"description": "返回结果数量限制",
"default": 10
},
"include_deleted": {
"type": "boolean",
"description": "是否包含已删除记录",
"default": false
}
},
"required": ["query"]
}
}7. 依赖注入
7.1 依赖系统设计
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 依赖注入流程 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
1. 定义依赖类型
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ @dataclass │
│ class MyDeps: │
│ db: Database │
│ api: APIClient │
│ user_id: int │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
2. 创建 Agent 时声明
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ agent = Agent( │
│ 'openai:gpt-4o', │
│ deps_type=MyDeps, ◄── 声明类型 │
│ ) │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
3. 工具中通过 RunContext 访问
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ @agent.tool │
│ async def my_tool( │
│ ctx: RunContext[MyDeps] ◄── 类型化 │
│ ) -> str: │
│ user = ctx.deps.db.get_user( │
│ ctx.deps.user_id │
│ ) │
│ return user.name │
└───────────────────┬─────────────────────┘
│
▼
4. 运行时传入依赖实例
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ result = agent.run_sync( │
│ 'prompt', │
│ deps=MyDeps( │
│ db=my_db, ◄── 实例注入 │
│ api=my_api, │
│ user_id=123, │
│ ) │
│ ) │
└─────────────────────────────────────────┘7.2 RunContext 详解
python
from pydantic_ai import RunContext
class RunContext(Generic[DepsT]):
"""运行时上下文"""
# 依赖实例
deps: DepsT
# 当前使用的模型
model: Model
# Token 使用统计
usage: Usage
# 消息历史
messages: list[Message]
# 工具名称(仅在工具执行时可用)
tool_name: str | None
# 重试次数
retry: int8. 与 LangGraph 架构对比
8.1 设计哲学对比
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 架构设计对比 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ │
│ PydanticAI LangGraph │
│ ───────── ───────── │
│ │
│ 声明式 图式 │
│ Declarative Graph-based │
│ │
│ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ │
│ │ Agent │ │ Graph │ │
│ │ │ │ │ │ │ │
│ │ ┌───┴───┐ │ │ ┌────┼────┐ │ │
│ │ │ Tools │ │ │ │ Nodes │ │ │
│ │ └───────┘ │ │ │ ↓ │ │ │
│ │ │ │ │ Edges │ │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ │ └─────────┘ │ │
│ └─────────────────┘ │
│ 隐式控制流 显式控制流 │
│ (框架管理) (开发者定义) │
│ │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘8.2 组件映射
| PydanticAI 概念 | LangGraph 对应概念 |
|---|---|
| Agent | StateGraph |
| Tool | Node (tool node) |
| RunContext | State |
| output_type | State schema |
| @agent.tool | @tool decorator |
| run() | graph.invoke() |
| run_stream() | graph.stream() |
8.3 适用场景
PydanticAI 更适合:
─────────────────
✓ 快速原型开发
✓ 简单的单 Agent 应用
✓ 强调类型安全的项目
✓ 需要结构化输出的场景
✓ FastAPI 项目集成
LangGraph 更适合:
─────────────────
✓ 复杂的多 Agent 协作
✓ 需要精确控制执行流程
✓ 有复杂状态管理需求
✓ 需要人类介入的工作流
✓ 企业级应用编排9. 小结
PydanticAI 的架构设计体现了以下核心原则:
- 类型优先:从底层到顶层全面使用 Python 类型系统
- 简洁 API:隐藏复杂性,暴露简单接口
- 可组合:工具、依赖、输出类型可自由组合
- 可观测:内置追踪和调试支持
- 灵活性:多种执行方式满足不同需求
与 LangGraph 相比,PydanticAI 选择了不同的权衡:
- 牺牲部分控制粒度,换取更简单的 API
- 牺牲部分灵活性,换取更强的类型安全
- 隐式执行流程,换取更快的开发速度
在下一章中,我们将深入探讨 PydanticAI 的核心概念:Agent、Tools、Dependencies 的详细使用方法。